DIRECTION
CONTROL:RATCHETS
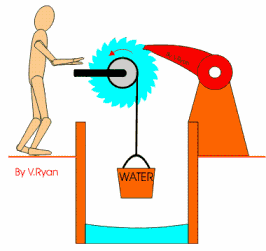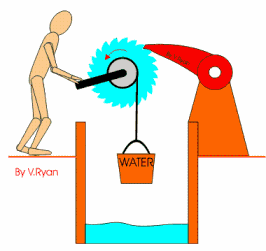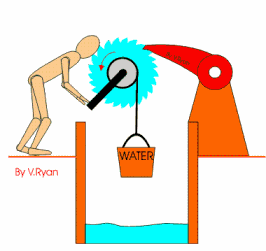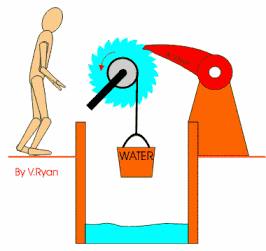
A ratchet is a mechanisms
that controls the direction of motion. It allows motion in one direction, but
not in the other, as you can see the
picture.
Some ratchets are
reversible, so they can turn and loc in one direction to another.
SPEED REDUCTION:BRAKES
Brakes use friction to
reduce speed. They are activated by certain levers. The lever transmits forcé
to an output receptor, which puts pressure on the Wheel. This produces
friction, which slows down the Wheel.
There are various types
of brake systems according to where the friction is produced:
Ø Disc brakes: A disc is connected to an axle. Brake
pads apply pressure to the disc.
Ø Brand brakes: A drum is connected to an axle. A
fexible band applies pressure to the outside of the drum. These brake were used
in carriages and they depended on the sttrength of the driver.
Ø Drum brakes: A drum is connected to the axle. A
pair of brake shoes apply pressure to the inside of the drum.

